Data Comm
Lab Test: Gigabit Ethernet Backbone Switches
Publication Date: November 1998
Test Outline
Copyright © 1998 by CMP Media Inc. Vendors are
encouraged to comment on this document and any other aspect of test
methodology. However, Data Communications and NSTL
reserve the right to change the parameters of this test at any time.
1 Introduction
This document
describes test procedures to be used in an evaluation of gigabit Ethernet
backbone switches to be conducted by NSTL Inc.. The test will measure the
performance of the products submitted for testing at layer 2 and when offered
at layer 3. NSTL will use the Netcom Systems Smartbits testers running the
Advanced Switch Test (AST) for gigabit Ethernet. Some routines will be built
using SmartWindows for Gigabit Ethernet.
2 Product
requirements
2.1 Gigabit
backbone switch tests
Participating
vendors must supply at least one backbone switch chassis. The test will be run
on a minimum of 8 interfaces. Tests will also be run on up to 24 interfaces if
the device under test (DUT) supports that number of interfaces. Products should have IP routing
capabilities.
3 Backbone
switch tests
The purpose of these
tests is fully exercise the gigabit Ethernet backbone switches to determine
their switching performance and behavior.
3.1 Forwarding
rate tests
3.1.1 Test
purpose
The purpose of these
tests is to determine the ability of the DUT to forward frames without loss at
line-rate loads on 8 ports and up to 24 ports if the DUT allows
3.1.2 Test
parameters
Number of ports: 8 minimum, tests also
conducted on up to 24 full duplex Gigabit Ethernet interfaces, depending on the
number of interfaces available on the DUT
Frame sizes: 64- and 1518-byte frames
Load: 100% loads will be offered. If the DUT
drops frames at this load level, the lab will drop back to 90 percent and, if
necessary, 80 percent loads
3.1.3 Test
metrics
Frame loss,
throughput and forwarding rate will be measured on all outbound ports.
3.1.4 Test
to be run
Non-meshed and fully
meshed streams of frames will be offered to the gigabit Ethernet interfaces of
the system under test (SUT)
3.2 Layer
3 packet forwarding rate
3.2.1 Test
purpose
The purpose of this
test is to determine the ability of the system under test to forward IP packets
between different subnets situated on each one of the Gigabit interfaces of the
DUT.
3.2.2 Test
parameters
Number of ports: 8 minimum, tests also
conducted on up to 24 full duplex Gigabit Ethernet interfaces depending on the
number of interfaces available on the DUT
Frame sizes: 64- and
1518-byte frames
Load: 100%loads will be offered. If the DUT
drops frames at this load level, the lab will drop back to 90 percent and, if
necessary, 80 percent loads
3.2.3 Test
metrics
IP packet loss,
throughput and forwarding rate will be measured on all outbound ports.
3.2.4 Test
to be run
Non-meshed streams
of IP packets with different source and destination subnet addresses will be
offered to the gigabit Ethernet interfaces of the DUT.
The gigabit Ethernet
interface for the Netcom Systems Smartbits is a layer-2 device. However, it
does allow creation and generation of packets with IP headers. Vendors will be
required to statically configure ARP tables in the DUT.
3.3 Broadcast
forwarding tests
3.3.1 Test purpose
To evaluate the
ability of the device under test (DUT) to forward streams of broadcast traffic
3.3.2 Tests
parameters
Number of ports: 8
gigabit Ethernet ports
Frame size: 64-byte
frames
Load: 100%loads will be offered. If the DUT
drops frames at this load level, the lab will drop back to 90 percent and, if
necessary, 80 percent loads
3.3.3 Test
metrics
Both broadcast
forwarding rate and broadcast latency will be measured
3.3.4 Tests
to be run
Offer broadcast
frames to one gigabit Ethernet interface addressed to all other interfaces on
the device
3.4 Address
handling tests
3.4.1 Test
purpose
To evaluate the
ability of the DUT to learn MAC addresses and to measure the DUT’s learning
rate and address capacity.
3.4.2 Test
parameters
The three test
interfaces will be gigabit Ethernet.
3.4.3 Test
metrics
The address learning
rate test will measure the maximum rate at which the DUT can learn new
addresses without dropping or flooding frames addresses to the newly learnt
addresses.
The address learning
capacity test will measure the maximum number of table entries the DUT can
register without dropping or flooding frames addressed to the newly learnt
addresses.
3.4.4 Tests
to be run
3.4.4.1 Address learning rate test
Offer 1024 new MAC
addresses to the DUT and through an iterative process determine the maximum
rate at which the device can learn them without dropping or flooding. This test
will be repeated with 2048 and 4096 new addresses. See AST documentation for
further details.
This test requires
the ability to set aging time on the DUT.
3.4.4.2 Address learning capacity test
Offer new MAC
addresses at the rate of 1000, or failing success 100 then 10 new addresses per
second and through an iterative process determine the maximum number of
addresses that the DUT can cache without dropping or flooding.
3.5 Head-of-line
blocking
3.5.1 Test
purpose
This test verifies
that a switch does not slow transmission or drop frames on interfaces which are
not congested whenever overloading on one of its other interfaces occurs.
3.5.2 Test
parameters
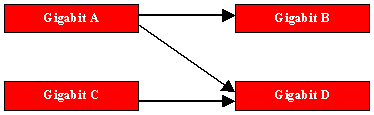
Offered 64-byte frame
load A to B equals 500 Mbit/s
Offered 64-byte frame
load A to D equals 500 Mbit/s
Offered 64-byte frame
load C to D equals 1000 Mbit/s
3.5.3 Test
metrics
Frame loss and
forwarding rates will be measured on outbound ports B and D.
3.5.4 Test
to be run
Traffic will be
offered to the interfaces of the DUT as indicated in the diagram below:
3.6 Route Lookup Performance
3.6.1 Test
purpose
The purpose of this test is to determine the
highest rate at which the DUT can look up a large number of arbritrary IP
destination addresses. This test is derived from the so-called Torrent test
(http://www.torrentnet.com/library/iclass.htm ), which exercises the route
lookup function by offering more than 1 million unique IP destination addresses
to the DUT. In the context of corporate campus backbone devices, devices are
more likely to look up hundreds rather than millions of unique addresses at any
given point. Accordingly, this test will offer up to 12,000 unique and random
IP addresses.
3.6.2 Test
parameters
Number of ports: 1 transmitting gigabit
Ethernet port, 4 receiving gigabit Ethernet ports
Frame size: 64-byte
frames
Number of unique IP
destination addresses offered: 4,096 first run; 12,000 second run
Unique address space:
172.16.0.0 to 172.16.15.255
3.6.3 Router
configuration:
Vendors should configure static routing tables
that distribute routes for 4,096 hosts among the four receiving ports, and
static ARP tables to handle IP-to-MAC address mapping.
For the routing tables, please configure the
DUT with addresses from the net 10 space:
Transmitting port:
10.0.1.1/24
Receiving ports:
10.0.2.1/24
10.0.3.1/24
10.0.4.1/24
10.0.5.1/24
Since there are four ports receiving traffic in
this test, each will act as a gateway for 1,024 host addresses.
We will use 10.0.X.254/24 as the default
gateway for each port, where X is the port number.
Vendors should also set up a static ARP table
for the five ports used in this test.
3.6.4 Test
metrics
The number of packets
received on the outbound ports will equal the number of addresses successfully
learned.
3.6.5 Test
to be done
Packets with unique IP
destination addresses will offered to one transmitting gigabit Ethernet ports
at line rate. A successful test will result in all offered packets being
delivered to the receiving ports without loss.
We will offer total of
4,096 unique host addresses, and if these are learned succesfully, repeat the
test with 12,000 unique addresses. The number of addresses is set in the
"cycle count" window of the Smartbits tester.
v. 1.03

